Brand Disruption: Be the Disruptor or Be Defeated
Disruption happens. In the world of brands, standing still is not an option. Recent events at Whole Foods Market have reminded us that brands are living entities. While every brand has a different lifespan, as with all living things, youth fades and the peak of health simply cannot last forever — brand disruption, time for a complete overhaul?
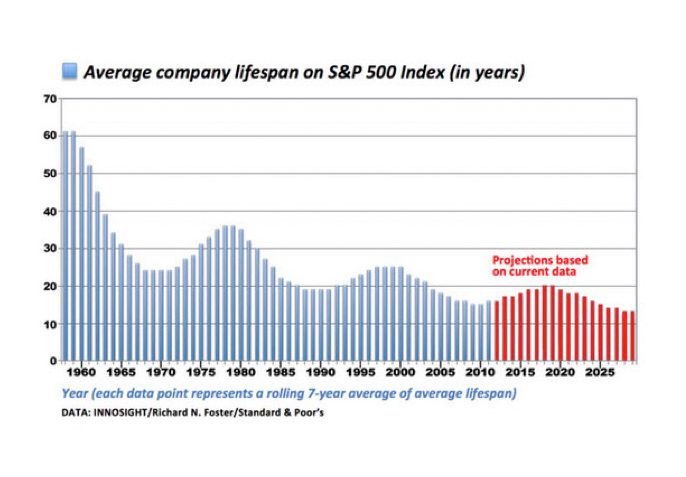
Image via Innospan
The average life of a company is a fraction of the 60+ years it realised following World War II, and it has been growing significantly shorter and shorter, now closing in on just 10 years which makes regular health checks even more critical to your brand’s survival.
“Change before you have to.” Jack Welch (Former chairman and CEO of General Electric, 1981-2001, during which time the company’s value rose 4,000%.) |
In the 2016 book, “Simplify: How the Best Businesses in the World Succeed,” the foreword opens with “…it is inevitable that sooner or later, someone will come along and revolutionise your industry…The good ol’ boys club rarely sees the outsiders coming until it’s too late.”
Related: The Power of Disruptor Brands and Challenger Brands
According to St. Gallen University in Switzerland, the basic business model is quite simple; it must provide answers to four questions. The answers will change — and must change — over time, or the brand will not survive.
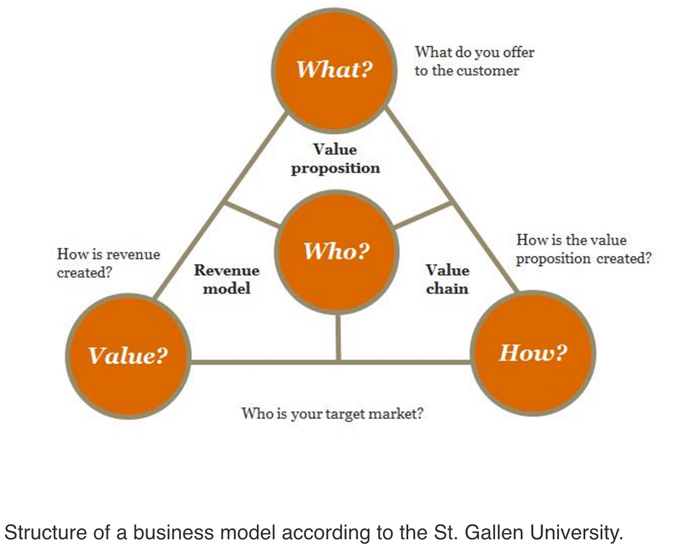
Image via St. Gallen University
Whole Foods: A Case Study in Brand Disruption
Whole Foods Market tells the story of their own modest first operation in Austin, Texas. “The original Whole Foods Market opened in 1980 with a staff of only 19 people. It was an immediate success. At the time, there were less than half a dozen natural food supermarkets in the United States.”[1]
Actually, Whole Food’s success story wasn’t at all an organic one. Growth came about in large part due to mergers and acquisitions in the USA, Canada, and United Kingdom. In effect, while Whole Foods disrupted traditional grocers, it was in the process of disrupting potential competitors within its own niche of natural, healthy, and organic foods. Over four decades, it certainly did grow. There are currently 87,000 employees and 466 Whole Foods Market stores.[2]
Now Amazon, the giant online shopping service which disrupted retail, is about to disrupt grocery, which had disrupted natural foods. In June 2017, Amazon filed a bid to acquire Whole Foods Market for $13.7 billion in cash.[3]
What happened?
Just a few years earlier in 2013, an ABC-TV news report heaped praise upon Whole Foods Market as “the grocer of the 21st century.” The interview with co-founder John Mackey mentioned “cult-like devotion,” saying “the place just looks delicious,” and “if you squint, the produce department resembles an edible Monet…”
However, things can certainly change fast in fast-moving consumer goods, right? Whole Foods lost almost half its value between October 2013 and July 2014.[4]
Related: Rebrand or Refresh? That is the Question
When Whole Foods Lost its Way
By 2015, it was apparent to all that trouble was brewing at Whole Foods. The “Whole Paycheck” moniker struck a chord…and it stuck. In addition:
- Customers took note when a massive overpricing scandal was revealed and settled for $500,000.
- Whole Foods received a warning letter from the Food and Drug Administration for a variety of hygiene problems at a food preparation facility.
- New York City Department of Consumer Affairs accused Whole Foods of systematic overcharging for prepackaged foods, calling it the worst case of mislabeling they had ever seen.
- Whole Foods apologised, but it was perceived as a weak apology, and the overpricing wasn’t easily shrugged off by consumers.
- Online food delivery had taken off and customers were shopping elsewhere where prices were lower.
Related: How to Manage, Survive, and Thrive
Earlier this year, a Barclays analyst issued a report estimating that Whole Foods lost as many as 14 million customers over the previous six quarters. “The magnitude of the traffic declines…is staggering. As most retailers know — once traffic has been lost, those patterns rarely reverse,”[5] said the bank.
Reportedly Whole Foods didn’t listen and learn. This week, an American financial news service reported that a basket of eight everyday food items purchased at Whole Foods cost $38.29; at Walmart, $19.86; and at Kroger, $16.58.[6]
Whole Foods pivoted somewhat in 2016, launching its own new, cheaper chain; but the change was too little, too late.
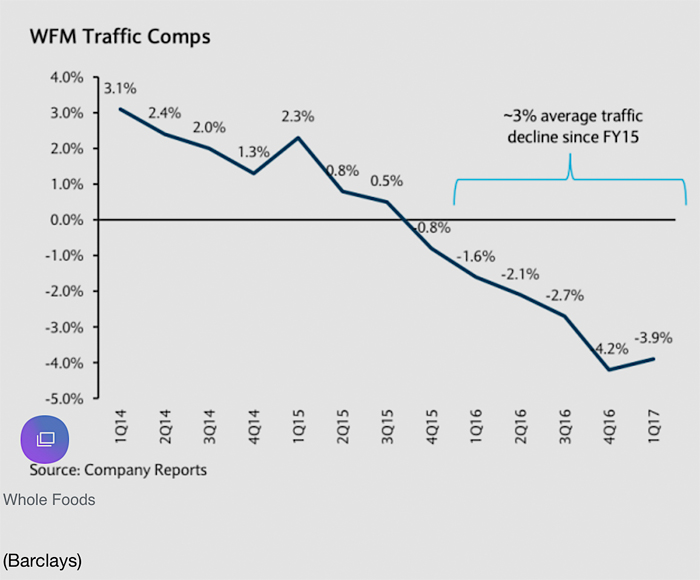
Image via WFM Traffic Comps, Barclays
Enter: Home Grocery Delivery On Demand
Look at the Whole Foods Market website home page. It mentions grocery delivery but doesn’t give it any emphasis.
Image via Whole Foods Market
Perhaps the grocery store was not seeing the potential in home delivery…potential that Amazon surely does? Whole Foods must have been aware of this, as they purchased an equity stake in Instacart[7], Internet-based delivery service — but not until 2016.[8]

Image via Ken, flickr 2.0
While Amazon / Whole Foods observers are saying that the logistics of perishable home grocery delivery (within two hours, please) are a nightmare,[9] let us recall milk truck deliveries. They certainly managed just fine without the benefit of high-tech.
Grocery shopping is a massive time waster. Driving to the grocery store, dealing with the parking, navigating the aisles, queuing up to pay, and lugging it all back home. However, the solution couldn’t be worth $13.7 billion — or could it?
Rather than internet-based home delivery of groceries, could the Amazon deal actually be about data acquisition? Or prime real estate that Whole Foods has cherry picked over the years? Or all of the above?
Only Jeff Bezos is likely to know which industrie(s) Amazon is about to disrupt.
Grocery Industry is Disrupted
Meantime, the planets are colliding in the home delivery business. Online groceries generated more than $15 billion in sales last year, which represented big growth but also represented a tiny fraction of the $1 trillion grocery market, according to Forrester Research.[10]
Disrupting Brand Disruption
Watch: “How Blue Apron Became a $3 Billion Company in 5 Years” by delivering pre-proportioned ingredients to customers’ doorsteps for around $10 a meal.
An impressive story…until the disruptor became disrupted by the Amazon / Whole Foods deal. “It was terrible timing for Blue Apron. Many potential investors quickly identified the possibility of more competition in the food-delivery industry and ran the other way,” reported Business Insider.[11]
Blue Apron gives us another example of how dramatic, dynamic, disruptive shifts can occur overnight for brands. The meals delivery startup was anticipating its own juicy IPO with a valuation of $3 billion in June 2017. Two weeks after the Amazon / Whole Foods surprise takeover announcement, Blue Apron’s valuation was slashed by more than one-third to $1.9 billion and shares opened flat at $10, down from an anticipated pre-IPO $17.
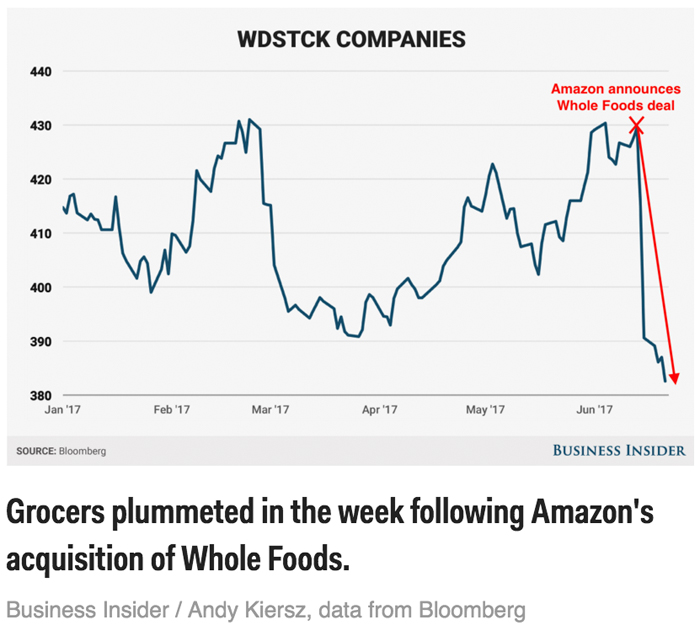
A group of large grocers: Walmart, Dollar General, SuperValu, Target, Costco, and Kroger (a.k.a. WDSTCK) — lost $24 billion in market value in the week following the Whole Foods deal.[12]
Following this Amazon filed a trademark for a meal kit service of its own knocking Blue Apron even harder — time to cook up a new highly innovative disruptive brand strategy!
Building Brands: Disruption is Ideation to the Nth Degree
Challenger brands have an important role to play by offering a superior product and satisfying customers. But not every challenger brand is a disruptor. And not every disruptor needs to tackle a huge industry sector. It all begins with an idea that clicks.
In 2010, Dollar Shave Club was aimed at a niche pain in men’s grooming — the high price of razor blades.
In San Francisco in 2007, Airbnb was born from the idea of two roommates sharing their air mattress and breakfast with out-of-town convention delegates to make a few bucks.
In Austin in 1980, Whole Foods Market was aimed at consumers of natural health foods — a very tiny niche.
In 2009, Uber realised that possession of a smartphone — but not a car — was central to the shared economy concept. Uber is currently at the top of the leaderboard for the world’s unicorns, that is, private startup companies with a $1-plus billion valuation.[13]
- Industries that have stopped innovating are prime for disruption.
- Market complacency is a telltale sign of a sector that’s ready for disruption.
- Services where customers voice frustration are prime for disruption.
Related: How Do Challenger Brands Become Market Leaders?
| “Something can be better, cheaper, and more convenient without being disruptive. The distinction, the one that people constantly miss, is that real disruption is almost impossible to see until it’s too late because the technology or business is so different from what already exists.” Business Insider |
In Silicon Valley, disruption is a buzzword. Examples of consumer brands litter the landscape, from travel, transport and accommodation to retailing and genetic testing — populating a rich list as well as the brand graveyard. For example, these remarkable stories have played out within just a few short years.
Related: 10 Branding Tips From Silicon Valley on How to Be a Successful Startup Brand
| Brand | Industry & Idea | Result |
| Dollar Shave Club | Men’s grooming. Home delivery of inexpensive razors and blades via membership club.
| Successful exit. Sold to Gillette (Unilever) for $1 billion within 5 years. |
| Airbnb | Hotels and travel. Changing how people think about accommodation via online listings at tariffs set by private hosts. | Backed by $2.5 billion in venture capital, still private, profitable. Operating in 65,000 cities, 191 countries. |
| Uber
| Public transportation, taxis, limousines. Rides on demand. | $66 billion valuation, still private, yet to make a profit. Co-founder and CEO fired after investigation into its corporate culture. |
| Theranos | Blood testing. Devices to automate and miniaturise blood tests using microscopic amounts. | From $4.5 billion to $0, a saga of controversy, allegations, failed lab inspections. Founder sanctioned. |
Ripe for Brand Disruption
In services, tech, consumer goods, and lifestyle, entrepreneurs are asking questions like these:
- What deep consumer frustrations are really behind the shocking behaviour we’re seeing in economy class on some of the world’s major airlines?
- Why has the cost of college more than doubled in 30 years and significantly outpaced inflation…and what can be done about it?
- What industries will the capabilities of 3D-printing disrupt first?
- When will we have a tiny battery that lasts?
- Can we develop a solution for non-invasive blood sugar level testing?
- What are the solutions for childcare and dual income, full-time working parents?
Are you feeling vulnerable in your sector? Are you equipped to make the requisite innovation and change to ensure your brand’s future relevance and success? Is it time to give your brand a health check to identify not only areas of strength and weakness but most importantly where the opportunities for potential innovation and growth exist.
If you want direction giving your brand a health check then take a look at our brand audit programme called the Auditing Analysis Accelerator™. This online course takes you through all the key steps you need to consider in giving your brand a health check. It enables you to identify areas of strength, weakness and pinpoint new opportunities for innovation and growth. You can watch a free course preview here.

Audit your brand now so you can identify where to innovate and ensure your brand is not disrupted!
So the questions in 2017 are;
- What industries need a top-to-bottom brand shakeup?
- What markets are ripe for brand disruption?
- What big problems are waiting to be solved?
- Where are the opportunities to fix what’s broken?
- Can you identify opportunities in your niche or in your community?
- Is it time to leverage a brand audit to help you identify strengths, weaknesses and areas for innovation and growth?
[1] http://www.wholefoodsmarket.com/company-info/whole-foods-market-history
[2] http://media.wholefoodsmarket.com
[3] http://media.wholefoodsmarket.com/news/amazon-to-acquire-whole-foods-market
[4] http://www.slate.com/blogs/moneybox/2015/02/11/whole_foods_q1_2015_sales_jump_as_wfm_prices_fall_and_customers_return.html
[5] https://www.inc.com/chris-matyszczyk/whole-foods-is-in-a-whole-heap-of-trouble-and-the-reason-why-is-surprising.html
[6] https://www.thestreet.com/slideshow/14185249/1/38-vs-20-groceries-comparison-shows-why-amazon-must-slash-whole-foods-prices-to-beat-walmart.html
[7] https://www.instacart.com
[8] https://www.thestreet.com/story/14194711/1/one-key-challenge-may-hold-back-amazon-and-whole-foods-back-from-crushing-the-grocery-store-industry.html?puc=yahoo&cm_ven=YAHOO&yptr=yahoo
[9] http://fortune.com/2014/04/04/next-up-for-disruption-the-grocery-business
[10] Ibid.
[11] http://www.businessinsider.com/blue-apron-ipo-public-company-amazon-stock-price-2017-6
[12] ibid.
[13] https://techcrunch.com/unicorn-leaderboard