Personal Branding: We Are All CEOs (Part 2)
In the second of a two-part post, we take a look at identifying your personal brand and maintaining it…and why personal branding no longer important just for celebrities or VIPs anymore.
To reinforce the message of this article Part 1, we reiterate: Everyone has a personal brand, whether they like it or not. To get the right personal brand so you can;
- Align yourself more effectively with your corporate brand
- Leverage yourself as an industry leader
- Mitigate risk in your business
- Get paid what you deserve!
- Manage your reputation
- Accelerate your career
- Get headhunted
you must map it out, create it to your liking, develop it and then nurture it.
Personal Branding – When the Brand is You
When Does Personal Branding Begin?
Good question. Actually, you’re never too young to begin personal branding. In our example from Part 1 of this article, we introduced Ryan. Ryan is 5 years old, has nearly 8 million subscribers, is the top money maker on YouTube, and is currently attracting more than $1 million per month from advertisers on his channel, Ryan ToysReview.

Image via Ryan’s Toy Review – YouTube
Fair enough, Ryan has built spectacular audience numbers for his personal brand over a two year period. Having said that, it does mean he got started at age 3!
Related: Personal Branding: We Are All CEOs (Part 1)
Some of the biggest YouTube celebrities are super young and successful. If you’re fine with being just a little bit jealous, check out these 13 pint-sized millionaires covered in a 2014 feature in Business Insider.[1]
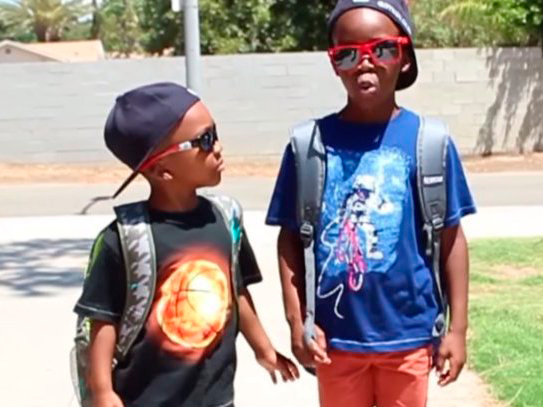

ZayZay and Jojo, 5 and 7, are huge on YouTube with millions of subscribers and views of their videos
However, personal branding isn’t just about one’s social media presence and a sales channel. So many early life choices about ourselves — our preferences in clothing, grooming, friendship circles, sports, hobbies — are actually branding at work as we mature and learn about ourselves.
In his TEDx talk at the University of California at Berkeley, Tai Tran talks about his personal journey from “zero to infinity.” Born in Vietnam to street vendors, new to the USA at age 6, he explains the why of building a personal brand — that it’s not what you know, it’s who you know by growing your network — and how to achieve your goals.
School Leavers Personal Branding: Your Personal Statement, Your CV, Your Network
In our final year of secondary school, we’re made keenly aware that a whole new world awaits. Whether it’s crafting a personal statement for a university application or writing a CV for employment or volunteerism, we are already putting a stamp on a personal brand.
A network of peers and mentors further defines your personal brand. By the time you’re preparing to leave school, you are expected to have gathered some reliable references who are happy to testify to that unique brand which is you.
Finding the Personal Brand at Your Core
Two popular 20th-century theories, Myers-Briggs and The Colour Code, both related to personality types have been widely embraced by individuals, educational concerns, and employers for several decades. There’s still some relevance in both these last century approaches so these exercises may help you determine your personal brand.
Related: Personality Matters, Bring Your Brand to Life to Grow Your Profits
Introduced in 1962, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator® identifies and describes 16 distinctive personality types based on preferences posed by 93 questions such as these.[2]
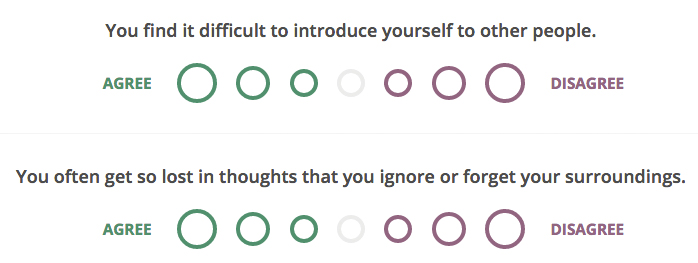
Image via myersbriggs.com
Personality type combinations derive from your tendencies, as follows.
Favourite world: Do you prefer to focus on the outer world or on your own inner world? This is called Extraversion (E) or Introversion (I).
Information: Do you prefer to focus on the basic information you take in or do you prefer to interpret and add meaning? This is called Sensing (S) or Intuition (N).
Decisions: When making decisions, do you prefer to first look at logic and consistency or first look at the people and special circumstances? This is called Thinking (T) or Feeling (F).
Structure: In dealing with the outside world, do you prefer to get things decided or do you prefer to stay open to new information and options? This is called Judging (J) or Perceiving (P).
These possible personality type combinations derive from your gut-reaction answers:[3] When you decide on your preference in each question, you have your own personality type, which can be expressed in four letters.
Back in 1987, Dr. Taylor Hartman created The Colour Code Personality Profile,[4] based on the principle of four key personalities, which he then organised into colour groups for ease of identification.
REDS
Need to look good technically, be right, and be respected. They are strong leaders and love challenges.
BLUES
Need to have integrity and be appreciated. They are focused on quality and creating strong relationships.
WHITES
Need to be accepted and treated with kindness. They are logical, objective, and tolerant of others.
YELLOWS
Need to be noticed and have fun. They love life, social connections, and being positive and spontaneous.
Reds
Reds are motivated by power. They are decisive and assertive. They’re planners. Problem solvers, adventurous and restless, planning for what’s going to be happening in the future. They are also great at solving problems and fixing situations. Reds are natural born leaders.
> Examples: Mark Zuckerberg, Angelina Jolie, Lebron James
Blues
Blues are driven by connecting and building relationships. They can be rather controlling in wishing to ensure everyone else is connected also, creating a potential clash with reds who don’t want to be controlled. Blues are people pleasers who can take critical feedback if it means being a more likable person. Blues are loyal; they remember names, dates and events.
> Examples: Oprah Winfrey, Mel Gibson in “Braveheart,” Forrest Gump character
Whites
People whose core colour is white are driven by peace – they really just want to get along but are often misunderstood. They are logical, passive, accepting, truthful, and tolerant. They may need to be asked for an opinion think and will frequently come up with amazing ideas when prodded a bit. Whites can are happy to work independently and avoid confrontations.
> Examples: John Lennon, Mahatma Gandhi, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.
Yellows
Yellows are the fun lovers, optimistic, spontaneous social butterflies. They’re carefree and enjoying the moment. Yellows let baggage go, they can easily erase things and move on. They are very curious people, like to learn new things and ask a lot of questions. Yellow have magnetic charisma.
> Examples: Ellen deGeneres, Will Smith, the Genie in Disney’s “Aladdin”
Dr. Hartman’s theory is supported by a 45-question free quiz, found here, intended to help you identify your personal brand.
Different Types of Offline Personal Brands
Your personal branding begins with your name. Although choosing your birth name wasn’t your decision, so much of your personal brand — how you appear to the world — is completely within your control.
These are a few examples of highly effective “types” you may model yourself on.[5] You may encompass one or more of them…indeed, the rare individual has something from all of these types.
As George Bernard Shaw said, “Life isn’t about finding yourself. Life is about creating yourself.”
- Youthful Excitement: You are daring, spirited, imaginative and up-to-date
- Authenticity: You are honest, genuine and cheerful
- Confident: You are tough, strong, outdoorsy and rugged
- Competence: You are reliable, responsible, dependable and efficient
- Elegant Sophistication: You are worldly, cultured, charming and glamorous
- Unique Persona: You are meticulous, independent, fearless and Persistent
- Zen Master: You are conscientious, observant, intelligent and humble
Different Types of Online Personal Brands
Faced with the prospect of online personal branding, some people protest, “Hey, I’m just a regular person!” No worries, that’s a type of personal brand, too.
Still, others say, “I don’t go online that much.” Neither good nor bad, such a behavioural choice also reflects your personal brand, frankly.
Take a look at these seven basic types of online personal brand[6] to determine where you fit.
1. The Content Creator
You’ve got talent. Whether your platform is YouTube, Instagram, Medium, your own blog or something else, you are known for producing terrific original content.
2. The Curator
Just like a museum curator, you assemble a collection of interesting stuff and share it widely. People follow you because you’ve got your finger on the pulse, even if you’re not the creator.
3. The Journalist
You can analyse and interpret without passing judgement. You’re part content creator and part content curator. You provide fact-based commentary and are a reliable voice; a go-to news source for your market or niche.
4. The Instigator / Critic
You play devil’s advocate and raise questions when other people don’t think to consider an alternative angle. You’re able to spark meaningful debate in your industry.
5. The Case Study
You’re the first to try things, an early adopter. People come to you as a good source to find out what works, what doesn’t, and why because they figure you’ve tested it.
6. The “Regular Person”
You let your personality shine through and it comes across as likable, genuine and authentic, even if you don’t consider your extraordinary in any particular field. Your brand is entirely built off you just being you.
7. The Industry Expert
You know your stuff inside and out. You’re widely considered a true professional in your niche and people turn to you for top notch advice.
Big or Small, Personal Brands Benefit From Care and Attention
Sure, life throws curve balls. But at the end of the day, you are the one responsible for making or breaking your own personal brand. No fabulous trophies or championship prize monies can do that on your behalf.
Related: Brand Sponsorships: The Best Ambassadors Are Already On Your Payroll
Tiger Woods: One of the world’s most successful golfers, a highly paid athlete and brand ambassador, has seen his brand fizzle under his own stewardship.
Related: Brand Crisis – How to Manage, Survive and Thrive
Case Study: Executive Chef Matthew Dolan
Executive Chef Matthew Dolan started working in kitchens as a dishwasher and a fry cook at age 14. In June 2016, his own top-class restaurant, 25 Lusk, was selected to host President Obama for a business leaders dinner in San Francisco.
Although Dolan humbly says, “I am a cook,” there’s a great deal more to it. Watch as Chef Dolan mentors Thunder, a former criminal, as a chef-in-training apprentice, changing the young man’s life in the process. The astute viewer observes that two personal brands are being shaped here.
Maintaining Your Personal Brand
It’s instilled in us from an early age that first impressions count and that we must maintain a good reputation. This applies to both online and offline interactions. Your personal brand is defined by your reputation, including other people’s perceptions of you, in everything you do, everyone you meet, everywhere to go.
If you want some direction mapping our your personal brand then take a look at our brand building programme called the Personality Profile Performer™. This online course takes you through all the key steps you need to consider in building your brand. You can watch a free course preview here.
Alternatively, if you want in-person professional direction and expert consulting support to build your brand and would like to discuss working with us then drop us a line to [email protected] or give us a call T: +353 1 8322724 (GMT hours 9:00-17:00). We’d be delighted to talk with you.
Controlling your personal brand must include awareness of your internet-based reputation. The management of your personal brand includes proper exposure across all internet “real estate.” Your professional website, social media profiles, photos, and published content should all reflect the brand promise you want to deliver.
Related: Brand Promises: How to Craft, Articulate and Live Them for Brand Success
Top 7 Tips for Developing and Maintaining Your Personal Brand
Fundamental to the process is your decision about exactly how you want to manage your social media outlets. Do you prefer to isolate Facebook for purely social reasons and use LinkedIn for your professional life? What about Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, YouTube and more?
- Photo: Ditch the sunglasses. Don’t use blurry images. Invest in a headshot that’s professional enough for your website and for LinkedIn A more relaxed profile image is appropriate for Facebook and other social media platforms whereas LinkedIn requires a more professional and groomed image — ladies don’t wear off-the-shoulder numbers on LinkedIn because it looks like you’re naked (unless that’s congruent with your personal and professional brand!) Pay attention to cover photo choices as well.
- Profile: Craft an elevator pitch. Make it brief enough for Twitter or for shaking hands in person when you’re asked: “What do you do?” It is intended to support your personal brand and strengthen your brand recognition. Write a succinct and compelling personal biography.
- Position: State your position. Reflect a personal brand philosophy that’s well defined and consistent in every piece of content that appears in connection with your name.
- Website: Build a quality website. It’s one of the first places you’ll be discovered online. Keep it vibrant, up-to-date, interesting and a positive reflection of your personal brand.
- Business cards: Ensure it’s consistent in messaging, language and design style with your other online assets, both social media profiles and website. Offer yours. It goes with a handshake, smile, and a look in the eyes. Even in the digital age, people still use business cards and yours should reflect your personal brand. It’s worth the extra effort and shows considered thought and preparation.
- Privacy: Stay secure. Double check your privacy settings on all platforms. The default may be to share with everyone, including those you are not connected with, and this may not be your preference. Best advice: Don’t post anything you’ll regret, especially as online privacy settings are frequently changing and old posts aren’t easy to cleanse.
- Network: Don’t hide. Make valuable connections. Join groups online and offline that reflect your interests and provide the right opportunities for supporting your personal brand and making connections within your niche.
Related: CEO Brand Leadership: How Vision Drives Brand Growth
Question to consider…
Is your personal brand the best it can be? Ask yourself the following six questions so you can evaluate, identify, develop and maintain your personal brand more effectively:
- If your personal brand isn’t altogether clear to you, how can you make it clear to others?
- How could you benefit from assistance in creating a personal brand?
- Is your personal brand consistent across all platforms, both online and offline?
- Have you set objectives for your personal brand?
- How confident are you that your personal brand will achieve its objectives?
- Does your personal brand need a health check?
[1] http://www.businessinsider.com/these-9-young-youtube-stars-are-all-becoming-household-names-2014-10
[2] http://www.myersbriggs.org/my-mbti-personality-type/mbti-basics
[3] MBTI® Manual: A Guide to the Development and Use of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator®
[4] https://www.colorcode.com/choose_personality_test
[5] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20140602153641-73005678-the-seven-types-of-highly-effective-personal-brands
[6] https://www.inc.com/nicolas-cole/there-are-7-different-personal-brand-archetypes-which-one-are-you.html





































-600px.jpg)























