The Age Of Internal Branding And Selling It From The Inside Out
Did you know that internal branding is the best way to get employees to develop a powerful emotional connection to your products or services so they become your top performing brand advocates because effective internal branding increases sales?
That emotional connection with the brand and its culture is what drives more than 2 million[1] people annually to apply to Google for a job.
Google is an unparalleled example of a brand which cultivates cult-like desire to work for them because candidates know that while Google only selects the creme-de-la-creme, the most elite top performers, the company also values their staff as their most important asset and looks after them accordingly. In short, Google understands the power of internal branding strategy, and selling the company from the inside out.
When staff are emotionally vested in the brand, they’re more loyal, motivated, productive, innovative, fulfilled and inspired by a unified sense of purpose.
Related: What’s a Cult Lifestyle Brand, and How do You Create One?
By applying branding principles from the inside first, employees glean a fuller knowledge of the brand and what’s important to it. Employees begin to “live” the vision of the company in their day-to-day tasks. And when employees live that vision in their roles the brand comes alive so your customers experience your brand’s promises to the full.
Related: Top 10 Brands for Customer Experience and What You Can Learn From Them
This article shares with you how to sell your brand from the inside out. But first, to make it more relatable so the theory is transformed into practical application take a look at this video which talks about the concept of internal branding.
The Link Between Employees and Internal Branding
Think about it for a moment, 60% of branding is about perception and only 40% about your product or service so one of the most significant factors influencing customers choices is how they perceive, think and feel about your brand through their interactions with it.
Contrary to what many think, branding is not just a logo or the aesthetics of a company’s website. Branding is the core DNA of your company – what makes it tick, the driving purpose behind everything you do and how you express your stand out brand personality at every touchpoint to engage your customers emotionally.
Because it’s only when you touch the heart that you move the mind so transforming your customers into committed fans, enthusiastic referral partners, word-of-mouth advertisers and repeat purchasers.
Anthony Robbins explains how emotions influence and drive all purchasing decisions masterfully here.
Related: Personality Matters: Bringing Your Brand to Life to Grow Profits
If you want some direction developing your brand and your internal branding then take a look at our brand building programme called the Personality Profile Performer™. This online course takes you through all the key steps you need to implement in building your brand. You can watch a free course preview here.

Build Your Profitable Brand Using The Personality Profile Performer™ Programme with Lorraine Carter
Alternatively, if you want in-person professional direction with expert input to develop your brand and internal branding and would like to discuss working with us then give us a call T: +353 1 8322724 (GMT hours 9:00-17:00) or drop us a line to [email protected]. We’d be delighted to talk with you.
Employees Are Your Internal Brand
The 2016 Edelman Trust Barometer confirms that people trust what employees say about the company more than they trust what the company says about itself. Trust is central to every brand because, without it, people will not buy from you.
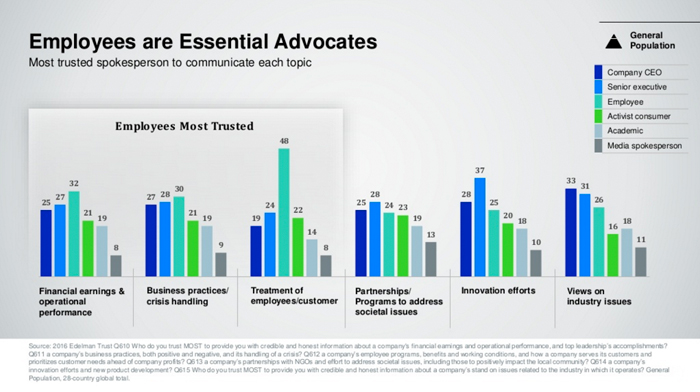
Image via Edelman Insights
When do employees represent, express, becoming living evidence of and talk about your brand? Front-facing staff represent your brand through their interactions with your customers. Non-front facing staff represent your brand when they discuss your company with friends and family and chat about their day on social media. Employees chat amongst themselves about your company — the good, bad and ugly.
Consider this, most of your employees are on social media and are either phenomenal ambassadors for your brand, indifferent workers clocking in time or worse still major detractors undermining your brand reputation.
Related: Top 10 Tips For Managing Your Brand Reputation
The ripple effect and network of influence per employee is extraordinary. It’s up to you to harness this for the greater good with strong internal branding or, through negligence, be at the mercy of come what may. At the very least make brand induction and training integral to what you do so you ensure your team are empowered, feeling and talking positively about your brand. In order for this to occur, your staff need to:
- Express your brand and what it stands for, or aims to stand for — a traditional mission statement won’t cut it because it lacks real-world application
- Identify how their behaviour supports or detracts from the brand
- Synthesise and consequently feel highly motivated to choose the right behaviour for the positive growth of the brand
At its most basic, this is how employees are integral to the internal branding of your company, which sells from the inside and extends to the outside.
Related: Socially Empowered Employees: Are They Key to Building Your Brand Online?
A Common Problem With Internal Branding
The problem is that few leaders understand the need or know how to convince employees of the brand’s “goodness”. Dangerous assumptions including thinking that employees are naturally attached to the brand. This couldn’t be further from the truth.
Related: CEO Brand Leadership: How Vision Drives Brand Growth
Leaders often operate with the mindset that staff are getting paid to do a job and that should be motivation enough. The truth is, if you want a higher performing company, a culture of innovation and growth with increased sales, you have to promote your brand to your employees first through an internal branding strategy, because they are an extension of your brand and take your brand to the outside world.
Related: The Case for Brand Disruption: Be the Disruptor or Be Defeated
The How Of Selling Your Brand From The Inside Out
Going Deeper Than Traditional Vision, Mission and Values
Internal branding is far more than wall hanging statements with the vision, mission and values expostulated on them. If you really want to impact behaviour favourably, you need to develop a culture around your brand vision, mission and values in a relatable, actionable sense so it’s a living expression, on a daily basis, of what you stand for.
Because when a company desires a specific culture that nurtures the positive behaviour of both leadership and employees, it must be carefully developed through brand profiling and brand strategy development. Otherwise, the vision, mission and values end up being superficial nonsense which a best delivers no meaningful or measurable results or worst still undermines the business.
When employees truly buy into your brand vision, mission and values, it drives their behaviour, commitment, performance and sense of fulfilment. In order to achieve this, they need to understand and value how their role in the company fits into and contributes to the overall goals of the business.
Related: Brand Sponsorships, The Best Brand Ambassadors Are Already On Your Payroll
An example of going deeper than a mere superficial listing the company’s vision, mission and values is Teva Pharmaceuticals.
In 1901, three gentlemen started a small wholesale drug distribution centre in Jerusalem.

The beginning of what would become Teva Pharmaceuticals in 1901. Image via Teva
Eventually, they moved into drug manufacturing, and between 1980 and 2000, they grew internationally. Today, they are the largest generics pharmaceutical company in the world.
In 2016, with more than 43 000 employees, Teva Pharmaceuticals embarked on a new brand identity strategy[2].
Beck Codner, Group EVP, Corporate Marketing and Communications, said, “Only when we are confident that all our employees are aligned around a shared purpose and how that should be reflected in how we think and how we act, will we be ready to externalise our new brand”.
As part of the new brand strategy, the Teva brand style guide and code of conduct was developed, so that employees would be well informed, empowered and armed with transparent standards to work with and represent the brand.

A screenshot of a section of Teva’s new code of conduct, based on their new internal brand strategy. Image Via Teva Pharmaceuticals
Watch Teva’s historical progress:
Focus On Marketing Your Brand Internally First
Whatever brand strategy, marketing or advertising you plan to activate externally, sell it to the inside first, and whatever communication is planned for your external market, customers and stakeholders alike, ensure you inform and induct your leadership team and employees first.
Why bother? Here’s one B2B example for the sake of clarity:
“Before you can do anything to gain success in your business, you’re going to need the buy-in and support of your team. A team is what grows the business. It’s not the technology; it’s not the computers.”
according to Yaniv Masjedi, Vice President of Marketing, Nextiva, a cloud based communication company.[3]
Image via Nextiva
In 2008, when Nextiva just opened its doors with a handful of staff, it was easy to keep people emotionally bonded to each other and the company. As it expanded to 300, with employees situated in other locations and many not knowing the names of fellow colleagues, it became necessary in 2012 to find a way to communicate company news more effectively, without resorting to the old fashioned newsletter.
“NexTV”, a weekly, internal video series was launched. They started small; each week, different employees would gather around a laptop camera to make announcements collected from all departments. Just 2 minutes long, it was uploaded onto YouTube – edit-free – for internal viewing. This killed two birds with one stone, so to speak because people in various locations could see the faces of fellow colleagues, some of whom they had never met, and get the news at the same time.
On average, 74% of Nextiva’s employees watch the series each week, with a 96% engagement rate.
The concept generates office fun and excitement, especially when employees know they’re being featured in the next episode.
Related: The Impact of Company Brand Culture On Driving Performance and Increasing Sales
In 2013, Nextiva started using more sophisticated means of internal communication, but the no-frills laptop camera method certainly achieved its purpose and has become a cornerstone of the company’s brand culture.
An example of one of the NexTV episodes.
Now logically, you’d think to sell change or marketing internally first, is a natural course of action, but for the majority of businesses, it’s not, because its importance is overlooked or forgotten. This is fatal for organisational goals, bottom line performance and sales growth.
Ensure management teams and staff are highly informed, fully engaged and relate to what’s happening before executing strategy externally, and if you make changes, be sure to sell it to them first.
Related: From Zero to Hero; How To Become a Must-Have Brand
Making Your Brand Come Alive for Staff Through Internal Branding
The point of branding – externally as well as internally – is to form an emotional connection with your ideal primary customer. This is why it’s no good simply documenting a dry vision, mission and values statement and filing it away or allowing it to become a wall dust-catcher because that accomplishes nothing. The vision, mission and values have to come alive for every staff member in order to increase performance and sales.
Related: Brand CSR: The Business Case for Successful Branding and Social Good
Staff have to live your brand and feel an emotional connection with it in order to sell it to your ideal customers whether in a formal work capacity or informally through their external life interactions.
Easier said than done; this section alone requires strategic thought: how do you make the brand come alive for your employees?
Firstly, the primary message needs to be introduced and the rationale behind it shared. This must be carefully developed because people are naturally resistant to change. When certain key factors are in place though, it makes the internal brand launch more readily received.
Secondly, the newly refreshed or revitalised brand message needs to be reinforced throughout employee touch points in daily activities. This needs to be strategically planned, just as you would plan a full-on customer marketing strategy.
Questions the brand strategy team needs to consider and plan around are:
- What do employees think of the brand and company?
- What do we want them to think?
- What will convince them of this?
- Why should they believe us?
Once these questions are evaluated and answered, the creation of internal branding collateral can be initiated. You don’t want to convey information, you want to persuade, emotionally engage and motivate. Make it actionable, fun, engaging and interesting.
Related: Brand Renaming: Name and Tagline Change Considerations
The Role of Communication In Internal Branding Strategy
It is often the HR department who execute internal communications when it should be the role of the marketing department who have the skill to market the brand not only to customers but to employees alike.
Communication is key internally, and yet the majority of businesses fail dismally at it.
In the 1980’s, HSBC, one of the largest financial organisations in the world, experienced rapid growth, and as a result, their employees became disconnected amongst themselves, the organisation and its leaders. In addition, the organisation had a traditional top-down approach, which made it just about impossible to obtain feedback from those on the ground. In today’s world, it’s not always an ideal model for a highly innovative, rapidly growing more progressive company which builds with high employee engagement.
The challenge was, how to get 250 000 people in one organisation, to be heard and feel their feedback mattered, and to change the traditional hierarchy?[4]
Enter Exchange Forum; the objective of which was to change the role of management.
Related: Brand Audits – How to Use One to Grow Your Profits
Internally known as the “shut up and listen” project, the forum was kicked off by holding meetings where management needed to “shut up” and listen to what their staff were saying, while saying nothing in return, so that the information would come from the bottom up instead of from the top down, recognizing that employees have opinions and knowledge that would be important to management decisions, especially for strategic changes.
The long term goal is that every employee should attend and participate in at least four “shut up and listen” exchanges each year.
Has the project worked? Take a look at this next video by HSBC titled, “through the eyes of our people”, and then answer this: from this video, does it appear as if employees feel connected now instead of disconnected?
Today, at HSBC, employees feel heard and leaders have learned the value of listening to what their team has to say.
Questions to consider with your internal branding
Is it time to sell your brand more strongly from the inside out? Consider these questions to improve clarity:
- Does your business sell its vision, mission and values to your employees first?
- Is your HR or Marketing department responsible for internal communications and are they integrated — working as a cohesive team?
- Can your staff and leadership articulate what your brand stands for and what makes you different to your competitors?
- Is your brand a living entity with a clear vision underlying at the heart of everything you do? Do your staff know how to incorporate the vision into their daily tasks?
Want to develop your internal branding strategy so you can build your team into your high performing brand champions but you’re not sure where to start to get a successful return on your investment?
Just drop us a line to [email protected] or give us a call T: +353 1 8322724 (GMT 9:00 – 17:00) — we’re here to help.
If you want direction and support transforming your internal branding strategy so it empowers your team and increases sales then the Persona Brand Building Blueprint™ Mastermind is the perfect fit for you.
This is a two-day brand building intensive shared with a small group of like-minded peers where you work on your brand with our leadership. In fact, over the two days, you reevaluate your brand, codify it and create your brand strategy from the ground up whether you’re revitalising an existing brand or creating a new one.
This is a highly empowering workshop where we take a deep dive, step-by-step into how to build a brand. You discover and apply the systems and methodologies used by some of the world’s greatest brands as you work on your brand under Lorraine Carter’s direction and tutelage so you can grow your own brand and business.
This is not a theory based program but a highly interactive fast-track course where you work intensively on your brand throughout the programme duration using our ten step system to:
- Completely re-evaluate your brand to make it much stronger so it’s highly visible enabling you to increase your profits
- Map out your brand in full so it’s codified and comprehensively documented to grow your business faster
- You leave with your total brand road map or GPS of your brand empowering you to manage your brand, stand out and attract your ideal customers so you multiply your sales
Outcome:
Your brand transformed so you can increase sales.
At the end of the two-day Persona Brand Building Blueprint™ Mastermind you leave with your fully documented brand strategy ready for implementation in your business or organisation.
Ring us to discuss your brand building preferences
Just drop us a line to [email protected] or give us a call T: +353 1 8322724 (GMT 9:00 – 17:00) to discuss your preferences and we’ll develop your brand building intensive bespoke to your particular brand requirements so that you’re empowered to develop and lead your internal brand building team.
[1] https://www.brazen.com/blog/archive/uncategorized/2-million-people-apply-work-google-year-heres/
[2] http://www.tevapharm.com/news/teva_pharmaceuticals_embarks_on_strategic_corporate_identity_program_to_build_a_global_brand_02_16.aspx
[3] https://www.marketingsherpa.com/article/case-study/internal-marketing-b2b-video
[4] http://www.gatehouse.co.uk/the-employee-communication-revolution-ripping-up-the-rule-book-at-hsbc/